The White House of the United States of America has published a Climate Resilience Game Changers Assessment, featuring 28 adaptation technologies, practices, and strategies for hardening the U.S. against climate shocks. As the title suggests, the assessment identifies “Climate Resilience Game Changers” that capture innovative, equitable, and scalable technologies, practices, and strategies that are ripe for research, development, and further investment by a wide range of stakeholders. Investing in, developing, and implementing the Climate Resilience Game Changers will strengthen human health and wellbeing, environment, economy, equity, and security.
A Climate Resilience Game Changer is defined as a practice, methodology, technology, or institutional, financial, or governance structure that (1) has been identified, prototyped, developed, or significantly refined in the last ten years, (2) has not reached the point of widespread adoption, and (3) if widely and appropriately adopted, would achieve or substantially advance one or more of the objectives of the American Climate Resilience Framework. The 28 game changers are organized across eight sector-specific categories that together account for the bulk of the U.S. economy, and four cross-cutting innovations: Nature-based Solutions, Information and Tools, Infrastructure, and Financing.
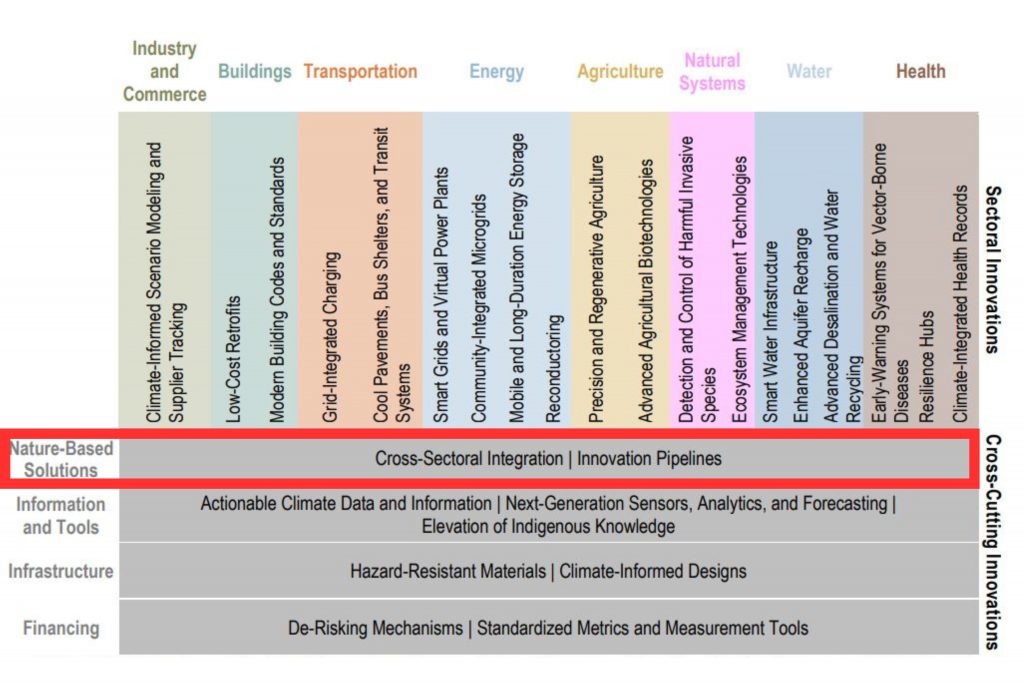
Even though Nature-based solutions (NbS) are increasingly considered in adaptation planning, their more systematic and equitable integration into relevant projects and decision-making processes would be a game-changing innovation, the assessment claims. As with the clean energy transition, strategic, purposeful, coordinated investment can accelerate new partnerships and rapid progress. Opportunities to promote cross-sectoral innovation include:
- Developing engineering guidelines, certification schemes, manuals, and standards to facilitate strategic deployment of NbS.
- Creating a comprehensive clearinghouse of high-quality NbS information and projects to facilitate partnership development, faster permitting, technical assistance, market viability assessment, and matchmaking to funding opportunities.
- Developing consistent approaches to facilitating NBS regulatory review and permitting, which may include regional partnerships, bundling of similar projects, and consideration of net social benefits of NBS strategies over their lifespans.
- Expediting environmental impact reviews and permitting for NBS at all levels of government, especially in response to time-sensitive needs (for example, before, during, and after emergencies occur).
- Creating new or improved research, decision-support, and technical tools […] for developing, monitoring, and evaluating NbS outcomes. Effective tools would include comparisons against alternatives, account for short- and long-term benefits, and account for particular benefits to communities with environmental justice concerns.
While many resilience practitioners already acknowledge that NbS can have benefits, gamechanging opportunities to build knowledge remain untapped in key areas. For example, targeted investments in research and development of NbS that are deployable at variable scales and geographies, as well as in monitoring and quantifying the longterm effectiveness of these projects, could make scaling and replicating NbS much easier. Establishing new NbS-focused research and extension institutes, NbS incubators, and NbS prize competitions targeted to this goal could drive collaborative action and signal demand to markets.
Investments could also establish new philanthropic or governmental NbS “test beds”. Supporting scalable NbS pilot projects would provide invaluable low-risk and high-value opportunities for modeling, monitoring, and demonstrating the value of emerging NbS applied across a range of environments. These “test beds” could also support the development of engineering standards that address performance, reliability, and maintenance costs.

